Research Everything IT
RECENTLY ADDED
Read the Latest in the Research Hub


Dec 23, 2025
Security
How Businesses Can Enhance Security and Deployments in Multi-OS Environments
Use Case
3 min
Discover how CDW helped a leading financial services company optimize device performance and streamline deployments within a mixed Windows and Mac ecosystem.


Dec 17, 2025
Security
How Businesses Can Enhance Security for Legacy Applications
Case Study
3 min
Discover how CDW helped a rural insurance provider modernize access for a legacy application that lacked support for current authentication methods.


Dec 10, 2025
Services
State and Local IT Funding: What Agencies Need To Know
Article
3 min
CDW Government can help you find the right funding to achieve mission success.


Dec 10, 2025
Services
How Federal Agencies Can Navigate Shifting Timelines
Article
4 min
Learn how CDW Government helps federal agencies stay agile and aligned with CIO priorities.


Dec 09, 2025
Data Analytics
Why Observability Is Replacing Rule‑Driven Data “Cleansing” and Why It Matters
Article
6 min
In this first blog of a two‑part series, we explain why continuous data observability is replacing rule‑driven data “cleansing” and why it matters.


Dec 09, 2025
Networking
Why AI for Networking Is Redefining IT Operations
Article
4 min
IT teams are moving from reactive troubleshooting to proactive optimization. Learn how organizations are adopting AIOps to simplify operations, reduce errors and prepare their networks for the future without replacing human expertise.
TRENDING
What Other IT Pros are Researching
View All

Sep 16, 2022
Networking
Why You Should Consider an Upgrade to Wi-Fi 6 or 6e
article
3 min
A wireless upgrade can help organizations meet users’ growing demand for connectivity.

Oct 03, 2022
Security
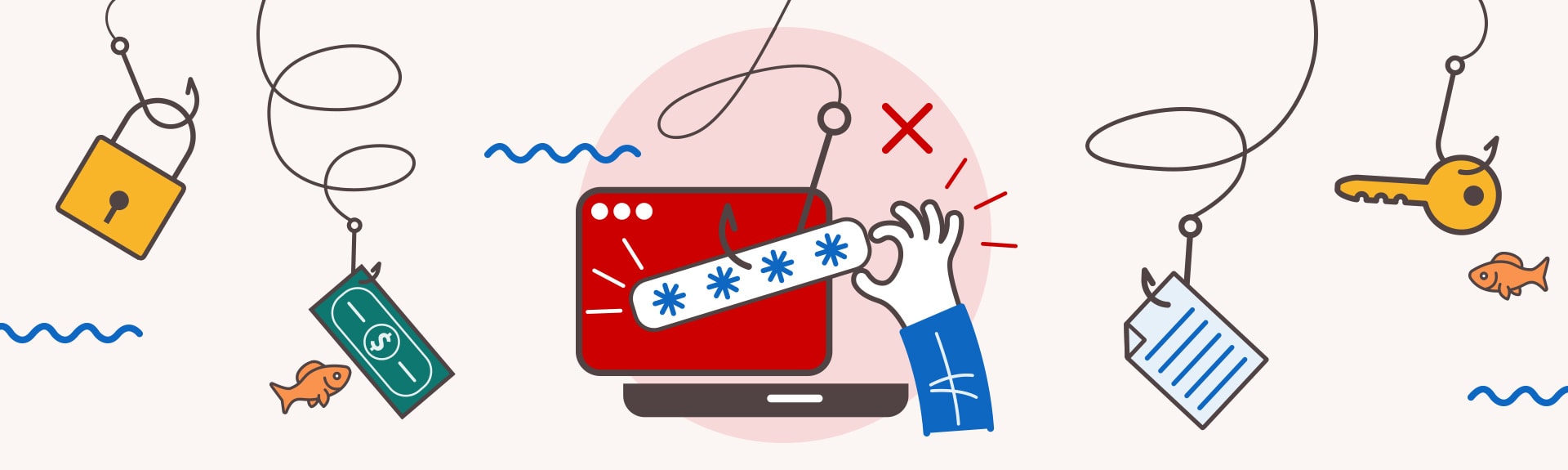
Don't Get Hooked: Avoid Becoming the Bait of a Phishing Email
article
3 min
Take a look at this infographic to learn what to look out for in a suspicious email.


Sep 23, 2022
Digital Workspace
Conversation Design Puts AI One Step Closer to Humans
article
4 min
Conversation interfaces can enable customer interaction with automated systems more naturally.


Sep 09, 2022
Cloud
When a DDoS attack comes, defend your applications with an AWS firewall
article
3 min
CDW Managed Services for AWS protects customer web applications using AWS WAF Security Automations.
SECURITY
Create a Secure Digital Environment
Helping to protect you—and your end users—from security breaches.


Dec 23, 2025
Security
How Businesses Can Enhance Security and Deployments in Multi-OS Environments
Use Case
3 min
Discover how CDW helped a leading financial services company optimize device performance and streamline deployments within a mixed Windows and Mac ecosystem.


Dec 17, 2025
Security
How Businesses Can Enhance Security for Legacy Applications
Case Study
3 min
Discover how CDW helped a rural insurance provider modernize access for a legacy application that lacked support for current authentication methods.


Nov 19, 2025
Security
Measuring the True Success of Your Vulnerability Management Program
Article
6 min
Are your vulnerability management efforts truly reducing risk or simply checking boxes? Learn to measure the success of your vulnerability management program with a tiered approach to metrics for operational, tactical and strategic insights.


Oct 30, 2025
Security
Secure the Unseen: Cracking the Code on Machine Identity Management
Article
5 min
Machine identities drive digital transformation but can pose security risks if left unmanaged. Effective management begins with a strong governance strategy, extending traditional IAM principles to address the unique challenges of machine identities.
Collaboration
A Digital Workspace for New Ways of Working
View All

Dec 09, 2025
Digital Workspace
How To Modernize Your Customer Contact Center To Meet Evolving Expectations
Article
5 min
AI-enhanced platforms, customer contact centers are rapidly evolving to make agents more productive and to provide a seamless customer experience.


Dec 05, 2025
Digital Workspace
How Workplaces — and the Technology That Supports Them — Have Evolved
Article
5 min
IT and business leaders must work strategically to meet employee expectations and reduce friction in the modern workplace.


Nov 28, 2025
Digital Workspace
Creating Seamless Personalized Journeys Across Every Channel
Webinar
1 min
Discover how to create a customer journey that makes every touchpoint feel effortless and human.


Nov 05, 2025
Digital Workspace
How Nonprofits Can Overcome Year-End Fundraising Challenges With IT Solutions
Article
4 min
Discover how nonprofits can tackle year-end fundraising with strategic IT solutions. From cloud collaboration to data security, learn actionable steps to streamline operations, deepen donor engagement and drive mission success during Q4.
CLOUD
Complete Your Cloud Journey


Dec 05, 2025
Cloud
How a Non-Profit Gained Autonomy and Agility With an Azure Cloud Migration
Case Study
4 min
Discover how CDW helped a non-profit organization migrate from a restrictive VMware environment to Microsoft Azure, reducing deployment times from one month to two hours and optimizing costs.


Dec 05, 2025
Cloud
Health Insurance Leader Scales for Future Growth With Cloud Adoption Framework
Case Study
0 min
Discover how CDW helped a major health insurer navigate market changes by implementing a Microsoft Azure cloud environment, reducing onboarding times by 98% and creating new revenue streams.


Dec 05, 2025
Cloud
Seamless Azure Migration Transforms Technical College’s Cloud Strategy
Case Study
3 min
Discover how CDW enabled a top-ranked technical college to migrate 76 virtual and nine physical servers to Azure with minimal disruption, enhancing scalability, efficiency and disaster recovery for better operational outcomes.


Dec 05, 2025
Cloud
Manufacturer Boosts VDI Performance With Azure
Case Study
4 min
A leading manufacturing company partnered with CDW to migrate its on-premises Citrix infrastructure to Microsoft Azure, eliminating performance issues and gaining scalability. See how the move improved user experience and reduced IT incidents.